4: Fatty acids. (A) Stearic acid (saturated). (B) Elaidic acid
Download scientific diagram | 4: Fatty acids. (A) Stearic acid (saturated). (B) Elaidic acid (unsaturated, trans). (C) Oleic acid (unsaturated, cis). from publication: Modeling of biomembranes: from computational toxicology to simulations of neurodegenerative diseases | It was known from the middle of the last century that a cell-membrane is a lipid bilayer. Since that time a large number of experimental studies has been done in order to see how a certain molecule can penetrate through a membrane. Due to the complexity of laboratory | Lipid Bilayer, Biomembranes and Membranes | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Molecular structure saturated unsaturated fatty acids glyceride esters biodiesel from vegetable oils waste fat transesterification advanced A level organic chemistry revision notes doc brown
Lipids

SOLUTION: Lipids mcq - Studypool
Reactions, Free Full-Text

Cellular Uptake, Metabolism and Sensing of Long-Chain Fatty Acids

Lipids - ScienceDirect

Draw the structure of the triglyceride formed from oleic acid, linoleic acid, and stearic acid. Give a balanced equation and show how much hydrogen would be needed to reduce the triacylglycerol completely.
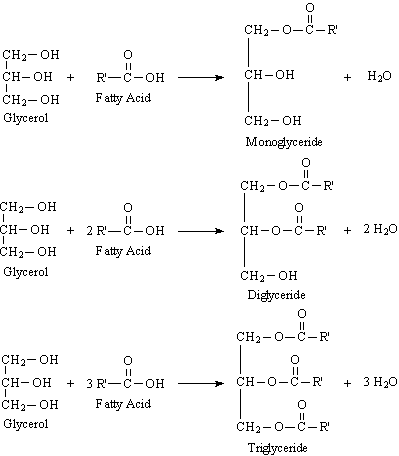
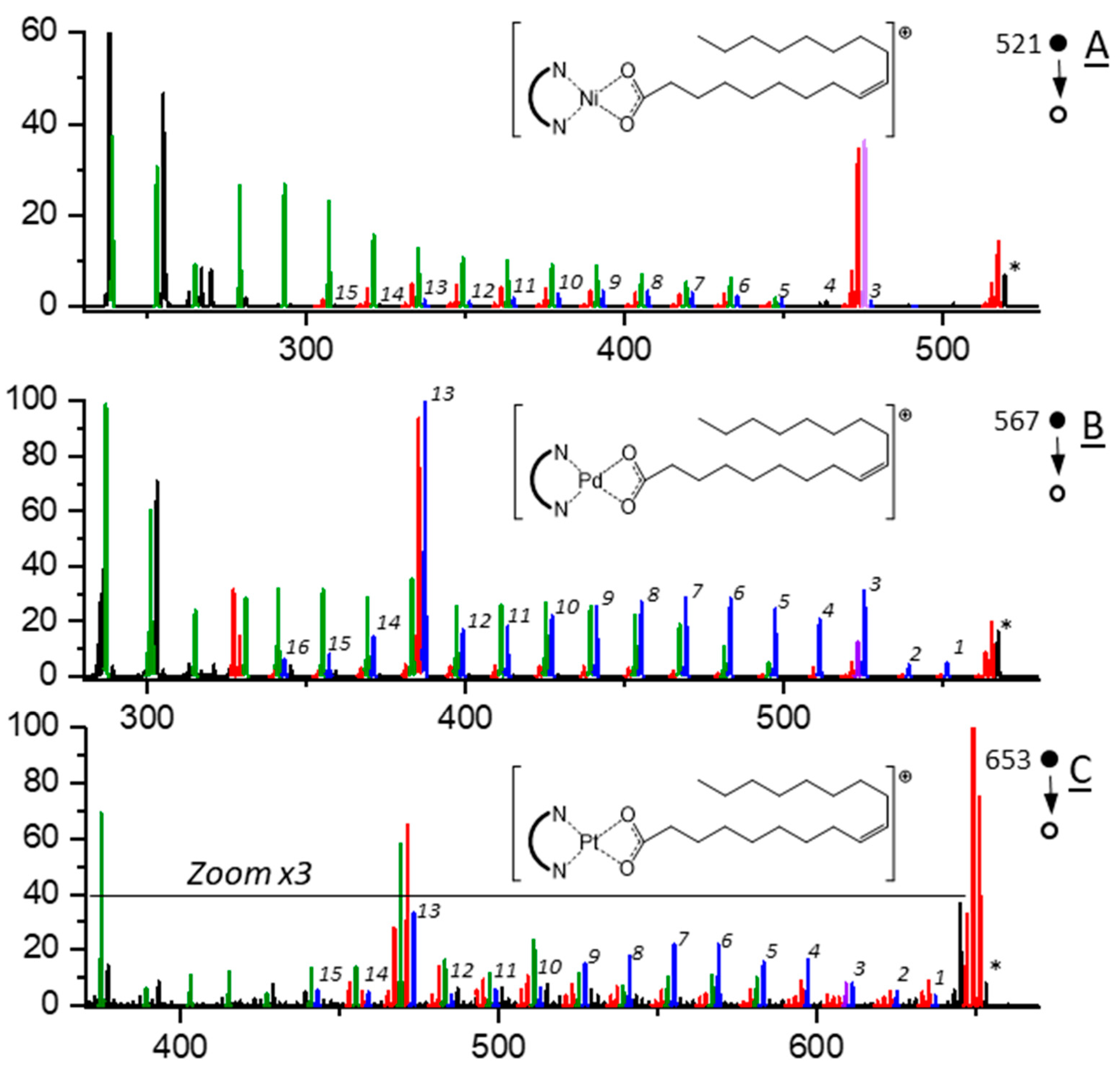
Lipids

PPT - Stearic acid PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:1797808
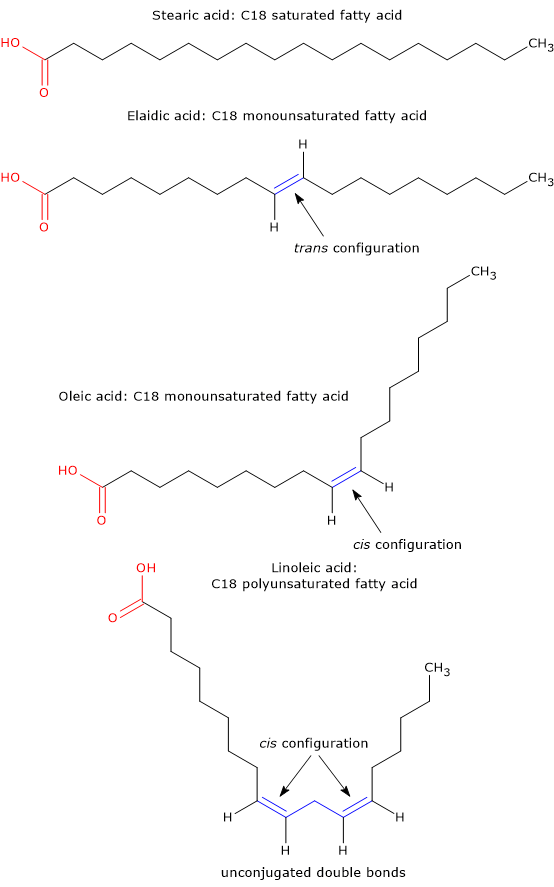
Fatty acids - Tuscany Diet

2.33 Fatty Acid Naming & Food Sources

Comparison of the Postprandial Metabolic Fate of U-13C Stearic Acid and U-13C Oleic Acid in Postmenopausal Women

Solved Consider these fatty acids : lauric acid: 1. Lauric

Some metabolic transformations of fatty acids: (A) the saturated fatty







